Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
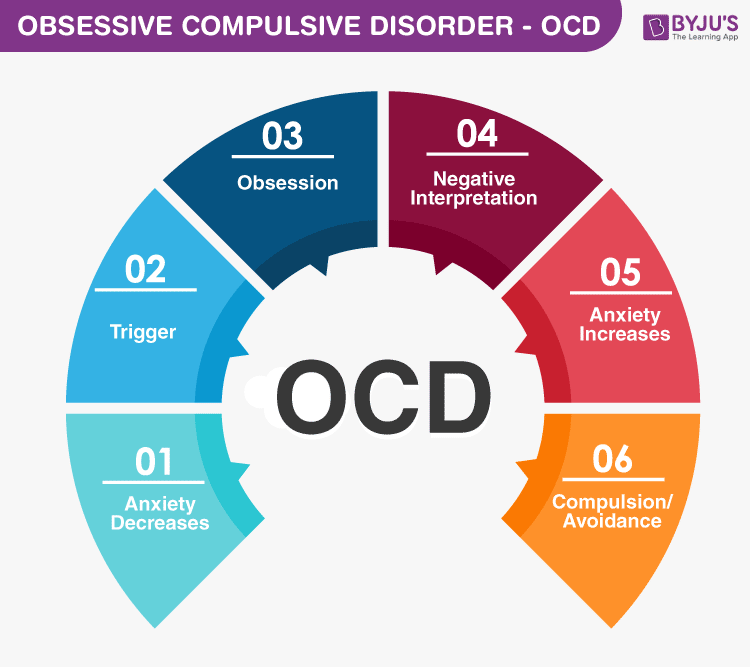
compulsive disorder (OCD) is a mental health condition characterized by persistent, intrusive thoughts (obsessions) that cause distress, leading to repetitive behaviors or mental acts (compulsions) aimed at reducing anxiety. These obsessions can range from fears of contamination to unwanted violent or intrusive thoughts, significantly interfering with daily life.
Compulsions, such as excessive hand-washing, ordering, checking, or mental rituals, are performed in an attempt to neutralize the distress caused by obsessions. However, these behaviors provide only temporary relief, reinforcing the cycle of obsessions and compulsions. Over time, this cycle can consume significant amounts of time and energy, impairing an individual's ability to function at work, school, or in personal relationships.
Effective treatments for OCD include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), particularly exposure and response prevention (ERP), and medication, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). These approaches aim to help individuals confront their fears without engaging in compulsions, ultimately breaking the cycle of OCD and improving their quality of life.
What are the symptoms of Obsessive Compulsive Disorder?
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is characterized by persistent, intrusive thoughts, images, or urges (obsessions) that cause significant anxiety or distress. Individuals with OCD often attempt to neutralize these obsessions by engaging in repetitive mental or behavioral acts (compulsions). Common obsessions include fears of contamination, harm, or a need for symmetry, while compulsions might involve excessive hand-washing, ordering, checking, or mental rituals. These symptoms can consume a significant amount of time and interfere with daily functioning, impacting work, social interactions, and overall quality of life.
Symptoms of Obsessive Compulsive Disorder in children
Intrusive thoughts, excessive hand-washing, repeating words, and repetitive behaviors.
Complications of Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
Physical damage, social and occupational difficulties, anxiety, and depression.
What causes Obsessive Compulsive Disorder?
The causes of OCD can be through genetics, and also environmental factors around the person.